The key to any successful rodent control program is identifying rodents\' entry points and sealing them. Regional Pest Management has been doing this procedure for over fifteen years.
Did you know that mouse can enter a structure with an opening a little larger than a quarter of an inch and a rat can enter with an opening of two inches? Most pest management companies will just find the entry points and ask the maintenance staff or homeowner to seal them. Regional Pest Management does it all for you—we identify the openings, then seal them with non-corrosive materials that stay in place wherever they are installed.
Ten Tips for Rodent Control
- Store garbage in metal or heavy plastic containers with tight lids.
- Place trash outside shortly before pickup; don\'t leave plastic garbage bags out overnight.
- Remove weeds and debris near buildings and in yards; don\'t give rats a place to hide.
- Store opened food in metal or glass containers with tight lids.
- Don\'t leave extra pet food out; store it in a secure container.
- Sweep up food remains, litter, and trash inside and outside your home.
- Inspect your basement and house for cracks and holes; seal them with mortar.
- Make sure you have screens on windows; inspect windows and screens for holes.
- Keep outside doors closed; use metal trim to prevent rodents from gnawing and entering underneath.
- Don\'t provide hiding places for rodents; store materials such as lumber and boxes on a rack with a clean, open area underneath. Get rid of unused materials and junk.
The House Mouse

House mice do not cause such serious health and economic problems as Rattus norvegicus and R. rattus. Mice are agricultural pests in some areas, however, and they do consume and contaminate stored human food with their droppings. They also destroy woodwork, furniture, uphostery, and clothing. In addition, they contribute to the spread of diseases such as murine typhus, rickettsial pox, tularemia, food poisoning (Salmonella), and bubonic plague.
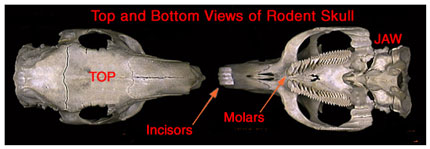
The house mouse (Mus musculus) is a small, slender rodent that has a slightly pointed nose; small, black, somewhat protruding eyes; large, scantily haired ears, and a nearly hairless tail with obvious scale rings. The adult mouse weighs about 2/5 to 4/5 ounces. Mice are generally grayish-brown with a gray or buff belly. Similar mice include the white-footed mice and jumping mice (which have a white belly), and harvest mice (which have grooved upper incisor teeth). Native to central Asia, this species arrived in North America along with settlers from Europe and other points of origin. A very adaptable species, the house mouse often lives in close association with humans and therefore is termed one of the "commensal" rodents along with Norway and roof rats. Following their arrival on colonists\' ships, house mice spread across North America and now are found in every state including coastal areas of Alaska, and in the southern parts of Canada.
Food Habits

House mice eat many types of food but prefer seeds and grain. They are not hesitant to sample new foods and are considered "nibblers," sampling many kinds of items that may exist in their environment. Foods high in fat, protein, or sugar may be preferred even when grain and seed also are present. Such items include bacon, chocolate candies, butter and nutmeats. A single mouse eats only about 3 grams of food per day (8 pounds per year) but because of their habit of nibbling on many foods and discarding partially eaten items, mice destroy considerably more food than they consume. Unlike Norway and roof rats, they can get by with little or no free water, although they readily drink water when it is available. They obtain their water needs from the food they eat. An absence of liquid water or food of adequate moisture content in their environment may reduce their breeding potential.
General Biology and Reproduction
House mice live in and around homes, farms, commercial establishments, as well as in open fields and agricultural lands. The onset of cold weather each fall in temperate regions is said to cause mice to move into structures in search of shelter and food.
House mice are mainly nocturnal, although at some locations considerable daytime activity may be seen. Seeing mice during daylight hours does not necessarily mean there is a high population present, although this usually is true for rats. Mice have poor eyesight, relying more on their hearing and their excellent senses of smell, taste and touch. They are considered essentially colorblind.
House mice can dig and may burrow into the ground in fields or around structures when other shelter is not readily available. Nesting may occur here or in any sheltered location. Nests are constructed of fibrous materials and generally have the appearance of a "ball" of material loosely woven together. These nests are usually 4 to 6 inches in diameter.† Litters of 5 or 6 young are born 19 to 21 days after mating, although females that conceive while still nursing may have a slightly longer gestation period. Newborn mice are naked and their eyes are closed. They grow rapidly and after 2 w3eeks they are covered with hair and their eyes and ears are open. They begin to make short excursions from the nest and eat solid food at 3 weeks. Weaning soon follows, and mice are sexually mature as early as 6 to 10 weeks old. Mice may breed year-round and a female may have 5 to 10 litters per year. Mouse populations can therefore grow rapidly under good conditions, although breeding and survival of young slow markedly when population densities become high.
House Mouse Behavior

During its daily activities, a mouse normally travels an area averaging 10 to 30 feet in diameter, seldom traveling further than this to obtain food or water. Mice constantly explore and learn about their environment, memorizing the locations of pathways, obstacles, food and water, shelter and other elements in their domain. They quickly detect new objects in their environment, but they do not fear novel objects, as do rats.
Regional Pest Management\'s Mouse Control Process
There are four basic steps to implement when confronting a mouse infestation:
- Inspection
- Sanitation
- Exclusion
- Population Reduction (Traps, Baits, Repellents)
In order for your rodent control program to be effective (as well as efficient) on a long term basis, all four basic steps should be implemented.
INSPECTION: When Regional Pest Management treats your mouse infestation problem, there ten signs we look for during initial (and follow-up) inspections: Droppings, tracks, gnaw marks, burrowing, runways, grease marks, urine stains, live or dead rodents, rodents sounds and rodent odors. Our inspection gives you a better idea of the size of the population and the routes taken by the rodents.
SANITATION: In order for a large population of rodents to flourish, there has to be an abundance of food and water, as well as easy access to a cozy nesting site. By removing or reducing the factors that make any pest population abundant, you remove and reduce the pest. This is the backbone of integrated pest management!
Sanitation does NOT imply that you live or work in a pig pen! Proper storage of possible rodent food, removal of undesirable vegetation (grass, weeds) and taking care of rubbish, lumber piles or old equipment are just a few examples of good sanitation practices. Homeowners must also realize that pet foods and wild bird feed are all tasty meals for rodents.
EXCLUSION: Controlling rats and mice by making it impossible for them to enter structures is the best way to eliminate and control indoor populations. Although this is not always feasible, exclusion should not be ignored. It is not always possible to do extensive rodent proofing, but in many cases it can be accomplished with minimum effort, and you can count on Regional Pest Management to point out to you how this may be done. A building can be rodent-proofed by eliminating all openings larger than 1/2 inch for rats and 1/4 for mice. Even after this is done, rodents can slip through open doors and windows, gain access along plumbing and other utility lines or (especially in the case of mice) be transported indoors with any merchandise. Exclusion also includes repairing doors and windows that do not operate properly or shut securely. Do not forget to inspect and repair air vents that may not be in sound working order.
POPULATION REDUCTION: To quickly reduce the population of mice, traps and/or baits are used. In some situations, the use of toxic baits are not safe, legal or desired because of possible odors. When dealing with mice, we prefer a combination of traps and baits if possible. We consider your building, the presence of children and pets, and the ability to deal with possible odors and dangers when choosing products to eliminate your mouse problem.
'; break; case 'rats': $title = 'Rats'; $banner = 'rodent-banner.png'; $content = 'The Black Rat (Rattus rattus)

The black rat is economically important in terms of damaging food stores and as a transmitter of diseases like the bubonic plague, typhus, food poisoning, and trichinosis. Rat-borne diseases are thought to have taken more human lives in the last ten centuries than all the wars and revolutions ever fought. One subspecies, Rattus rattus brevicaudatus, has even caused famines. It consumes and destroys food stores and carries epidemics and diseases with its fleas, urine, and dirt. Black rats gnaw through insulation from electrical wires, sometimes causing fires. They also kill poultry, domestic livestock, and game birds. Through predation and competition, they have contributed to the endangerment or extinction of many species of wildlife.
Rat Behavior
The black rat is active at dusk and during the night. Having a history of dependence on man, living in human communities, and competing with man for food may have led, by natural selection, to changes in behavior related to coexistence with humans. Rattus rattus, for example, display avoidance of unfamiliar objects such as traps. Living in trees or roofs, R. rattus tend to flee upward. These do not burrow or swim but climb and nest above ground. They construct a loose, spherical nest of shredded vegetation, cloth, or other suitable material.

The black rat is a territorial, sociable animal, sometimes forming clans of up to sixty animals. Social groups usually contain a single dominant male and sometimes a linear male heirarchy. There are also two or three top females, subordinate to the males but dominant to the rest of the group. Females display more aggressive behavior than males. The feeding territory is defended against outsiders by biting, jumping, and standing on hind legs and hitting with the front paws. The infants in the group have immunity from aggression and can take food from the dominant adults.
Rattus rattus are omnivouous. They eat seeds, nuts, vegetables, fruits, insects, invertebrates, and other materials such as soap, paper, hides, and beeswax. Food may be carried back to the nest and stored.Rat Elimination
There are four basic steps Regional Pest Management uses when eliminating a rat population:
- Inspection
- Sanitation
- Exclusion
- Population Reduction (Traps, Baits, Repellents)
In order for your rodent control program to be effective (as well as efficient) on a long term basis, all four basic steps should be implemented.

Inspection: There are ten signs we look for when conducting an initial (and follow-up) inspection: Droppings, tracks, gnaw marks, burrowing, runways, grease marks, urine stains, live or dead rodents, rodent sounds and rodent odors. A good inspection will give you a better idea of the size of the population and the routes taken by the rodents. As you will see in Population Reduction, you must intercept the rodents! Proper placements of baits, traps or live traps depend on proper inspection!
Sanitation: In order for a large population of rats to flourish, there has to be an abundance of food and water, as well as easy access to a cozy nesting site. By removing or reducing the factors that make any pest population abundant, we remove and reduce the pest. This is the backbone of integrated pest management! Sanitation does not imply that you live or work in a pig pen. Proper storage of possible rodent food, removal of undesirable vegetation (grass, weeds) and taking care of rubbish, lumber piles or old equipment are just a few examples of good sanitation practices. Homeowners must also realize that pet foods and wild bird feed are all tasty meals for rodents.† If rats have easy access to an abundance of dog food (especially at night when feeding is heaviest), they are less likely to be attracted to rodenticides or baited traps.

Exclusion: Controlling rats by making it impossible for them to enter structures is the best way to eliminate and control indoor populations. Although this is not always feasible, exclusion should not be ignored. It is not always possible to do extensive rodent proofing, but in many cases it can be accomplished with minimum effort. A building can be rodent proofed by eliminating all openings larger than 1/2 inch for rats. Even after this is done, rodents can slip through open doors and windows, gain access along plumbing and other utility lines or be transported indoors with merchandise! Exclusion also includes repairing doors and windows that do not operate properly or shut securely. Do not forget to inspect and repair air vents that may not be in sound working order.
Population Reduction: To quickly reduce the population of rats, we use traps and/or baits. In some situations, the use of toxic baits are not safe, legal or desired because of possible odors. When dealing with rats, we prefer a combination of traps and baits. We consider your building, children, pets, ability to deal with possible odors and dangers to non-target animals when choosing products to eliminate your rat problem.
'; break; case 'moles': $title = 'Moles'; $banner = 'home-service.png'; $content = 'Scalopus aquaticus (eastern mole)

Moles can do great damage to lawns, gardens, golf greens, farms, parks and playing fields. Here\'s a bit of information on just what they can do...
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Insectivora
Family: Talpidae
Subfamily: Talpinae
Genus: Scalopus
Species: Scalopus aquaticus

The mole, in its search for food, burrows in lawns and other areas where soil conditions are suitable. Moles are very active tunnelers and can tunnel at a rate of 12 to 15 feet per hour. In spring and fall, these burrows are just a few inches below the surface with the soil pushed up into ridges. In summer and winter, burrows are deeper with the only evidence being mounds of soil pushed up to the surface. Both types of burrows produce damage to the lawn or garden.
Geographic Range
Scalopus aquaticus is found from southeastern Wyoming, South Dakota, and central Texas east to Michigan, Massachusetts, and New England, south to the tip of Florida, and north to Ontario. The eastern mole prefers fields, meadows, pastures, and open woodland. It is not found in stony or gravelly soils or in clay but frequents moist, sandy, and loamy soils.
Physical Description
Head and body length in Scalopus aquaticus ranges from 110 to 170mm. Tail length ranges from 18 to 36mm. This size variation occurs on a gradient with the largest animals in the northeast and the smallest in the southwest. The robust body is covered with a thick velvety fur of a color that varies from silver to black to copper. The short tail is round, almost hairless, and indistictly scaly. The feet are scantily haired above, naked below, and quite large. The webbing between the toes of each foot aids in digging. These moles have no external eyes or ears. It is thought that the poorly developed eye may be effective in detecting light.
Reproduction
Breeding and parturition occur once a year in Scalopus aquaticus. Breeding takes place in late March and early April in most of this mole\'s range, but the season begins in January in the south. Estimates of gestation length range from four weeks to 45 days. Litters usually contain two to five young. The young moles are independent in one month and are sexually mature by the next breeding season. One captive animal lived longer than 36 months!
Behavior
S. aquaticus has daily activity peaks from 0800 to 1600 hours and from 2300 to 0400 hours. Male home range averages 1.09 hectares whereas female home range averages only .28 hectares. These moles are not solitary. Their home ranges often overlap and several individuals have been found using the same tunnel systems. These tunnels are found in two forms. One type consists of deep, fairly permanent passageways that are used as burrows and as routes to feeding sites. The other consists of surface runways used for collecting food. Winter tunnels tend to be deeper than summer tunnels. Nest chambers of dry vegetation are usually below the surface underneath a boulder or the roots of a plant. Eastern moles can dig up to 4.5 meters in one hour with their powerful forefeet. One individual dug 31 meters of shallow tunnels in one day. Special morphological developments enable the mole to burrow with such speed. Their forefeet are large and as wide as they are long. The bones of their shoulder girdles and upper forelimbs provide broad suraces for muscle attachment. When they burrow, these moles essentially "dive" into the earth; they first thrust their forefeet into the soil and then follow with the head and body as they rotate their forelimbs and pull the loosened dirt backwards.
Scalopus aquaticus has high energy requirements and needs considerable amounts of food daily. As a result this animal forages widely; the incidence of inbreeding is low and the level of gene flow is fairly high. These patterns are unusual for fossorial mammals. Soil type and moisture are the eastern mole\'s major barriers to dispersal. They are good swimmers and are limited not by water itself but rather by the moist, clay-filled soils that accompany water courses. Soil acidity, which determines food abundance, provides another potential barrier to dispersal.
Food Habits
Scalopus aquaticus eats primarily earthworms. It also eats insects and their larvae, some vegetation, and, in captivity, ground beef, dog food, mice, and small birds. Each day this mole eats 25 to 100% of its own weight in food. As an insectivore, this animal eats the larvae of many insect pests. It also helps to aerate and turn over the soil.
'; break; } ?>